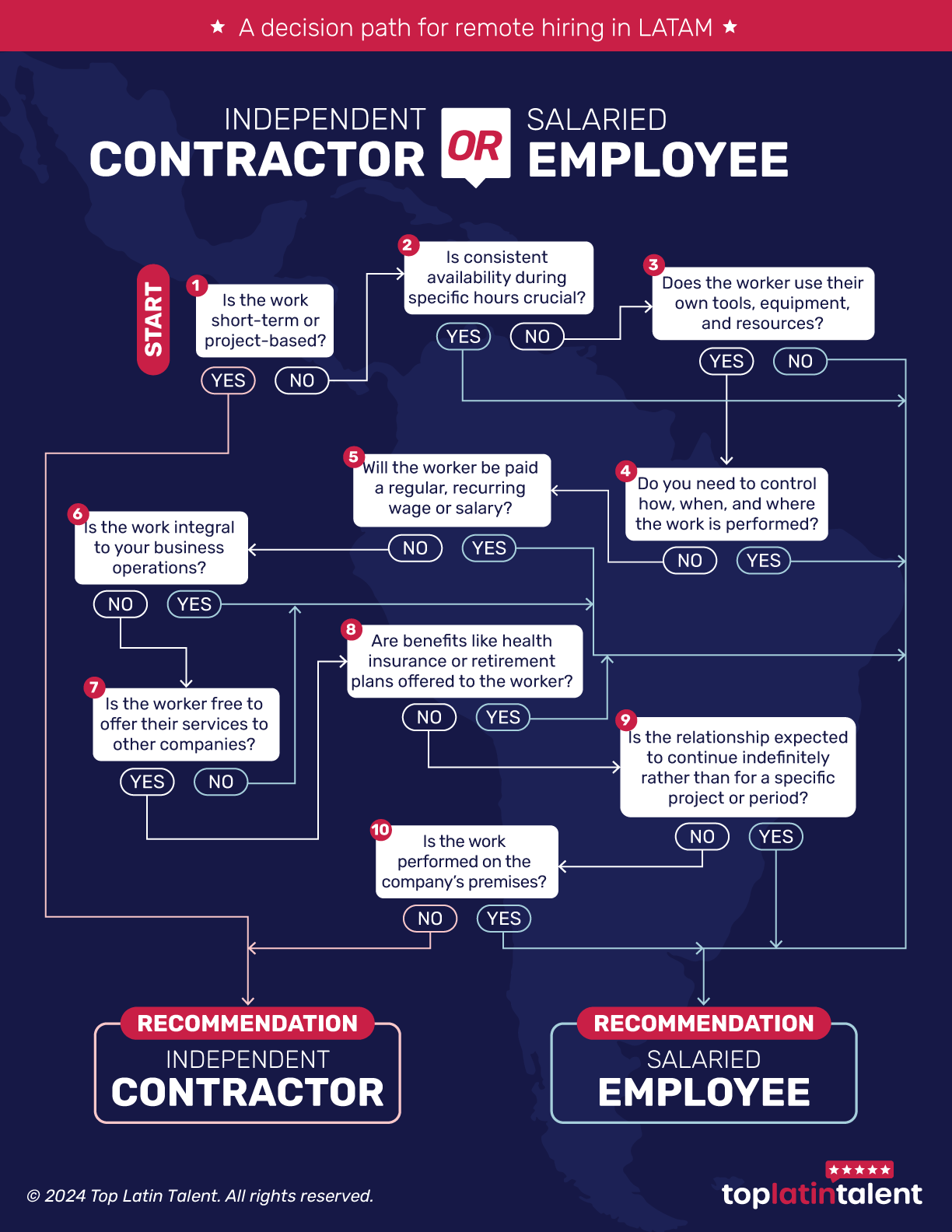
How to decide between hiring an independent contractor or a salaried employee for remote roles in LATAM

As businesses increasingly adopt remote work, hiring talent from Latin America (LATAM) offers a significant advantage. LATAM is home to a pool of skilled professionals with diverse expertise, often at competitive rates. When hiring remote talent from LATAM, deciding whether to opt for an independent contractor or a salaried employee is important. This decision impacts your company’s flexibility, budget, legal compliance, and overall success.
This guide will outline crucial factors to consider in making this decision and explore the pros and cons of each option. By the end, you will clearly understand how to align your hiring strategy with your business goals and legal requirements, ensuring a smooth integration of LATAM talent into your team.
Understanding the roles: independent contractor vs. salaried employee
Before making a decision, it’s essential to understand the fundamental differences between independent contractors and salaried employees.
Independent Contractors are individuals or entities hired to perform specific tasks or projects, typically for a limited period. They work with a high degree of autonomy, deciding how, when, and where the work is done. Contractors generally provide their own tools, manage their business expenses, and handle their taxes. They are usually paid per project or deliverable instead of receiving a regular paycheck. This arrangement is ideal for companies seeking flexibility, specialized expertise, and cost savings.
Salaried Employees are hired for long-term roles that are essential to the company’s operations. They are expected to work a set number of hours per week and generally have less flexibility in how they carry out their tasks. Salaried employees are provided with the necessary tools and resources and receive a regular paycheck, along with benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. This arrangement is suitable for companies seeking stability, consistent availability, and deeper integration into the company culture.
Key factors to consider when hiring in LATAM
When deciding between an independent contractor and a salaried employee, several factors come into play. Below, we’ll explore these considerations in detail to help you make an informed decision.
Duration of work
When deciding between hiring an independent contractor or a full-time employee, it’s important to consider the duration of the work. Independent contractors are usually brought in for specific projects with a definite end date, such as building a website or providing short-term consulting services. Once the project is completed, they are typically released.
On the other hand, if the work is ongoing and essential for the business’s day-to-day operations, a full-time employee may be more suitable. Roles involving continuous tasks like managing social media, providing customer support, or handling IT operations often require the consistent presence and performance that a salaried employee can offer.
Control and flexibility
Another critical factor is the level of control you require over the work process. Independent contractors offer a high degree of flexibility as they are self-directed and responsible for how they complete their tasks. This autonomy is advantageous if you need a specialist for a particular task without needing to oversee every step of the process. However, it’s important to avoid exerting too much control over a contractor—such as dictating their work hours or methods—because it can blur the lines between a contractor and an employee, leading to potential legal issues.
In contrast, salaried employees are expected to follow company guidelines and procedures, allowing you to exercise greater control over their work. If your business requires strict adherence to specific protocols or if you need to ensure that tasks are performed in a particular way, hiring an employee is likely the safer option. This approach reduces the risk of misclassification and ensures that the work aligns with your company’s standards and objectives.
Budget considerations
Budget is often a decisive factor when choosing between an independent contractor and a salaried employee. Independent contractors can be more cost-effective in the short term, as you only pay for the work delivered without the additional expenses of benefits, taxes, and overhead. This is especially beneficial for startups or small businesses with limited resources. Additionally, contractors can be hired as needed, allowing you to scale up or down depending on your project load.
However, while contractors may seem less expensive initially, it’s essential to consider the long-term costs. For ongoing work that requires regular attention, the cumulative cost of hiring contractors can exceed the cost of employing a full-time worker. Salaried employees, although more expensive upfront due to benefits and taxes, can provide more value over time, especially if their role is central to your business operations.
Confidentiality and integration
When it comes to roles involving sensitive information or requiring alignment with your company culture, hiring a salaried employee may be the better choice. Salaried employees are generally more committed to the company’s success, are likely to adhere to confidentiality agreements and company policies, and integrate well into the company culture, leading to improved collaboration, higher morale, and enhanced performance.
Independent contractors, while professionals in their field, may not demonstrate the same level of commitment to your company. As they often work with multiple clients, they may place less emphasis on cultural fit or long-term loyalty. If maintaining confidentiality and company culture are top priorities, hiring a full-time employee who can be fully integrated into your team is likely the safer and more effective option.
Legal compliance and misclassification risks
Legal compliance is one of the most critical aspects of deciding between an independent contractor and a salaried employee. Misclassifying an employee as an independent contractor can lead to significant legal and financial repercussions, including fines and penalties. Each LATAM country has its own guidelines for determining whether a worker is an employee or a contractor. These guidelines typically focus on factors such as the degree of control the company has over the worker, the financial relationship between the worker and the company, and the nature of the work being performed.
Understanding the labor laws in the LATAM country where you are hiring is crucial. Each country has its own set of rules regarding worker classification, employee rights, and tax obligations. Working with legal experts familiar with LATAM labor laws can help you navigate these complexities and ensure your hiring practices are compliant.
Common misclassification triggers
- Control over work details: If you dictate how, when, and where the work is done, the worker may be classified as an employee.
- Regular payment: Paying a fixed salary or regular wage can imply an employment relationship.
- Provision of tools/equipment: Supplying necessary tools or resources typically indicates an employee role.
- Integral role in business: If the work is a key part of your business, it’s often performed by employees.
- Exclusivity: Limiting the worker’s ability to work for others can suggest employee status.
- Offering benefits: Providing benefits like health insurance strongly indicates an employee classification.
- Long-term relationship: An ongoing relationship beyond specific projects leans towards employee status.
- On-site work: Regular work on company premises often implies an employment relationship.

Industry-specific considerations
Different industries have varying needs when it comes to hiring talent. Let’s explore how the decision to hire an independent contractor or a salaried employee might differ across some common industries.
Technology and IT
Independent contractors are often hired in the tech industry for specialized tasks such as software development, cybersecurity audits, or IT infrastructure setup. These roles typically require specific expertise that may not be needed full-time. For example, a company might hire a contractor to develop a new application or to perform a one-time security assessment.
However, a salaried employee may be more suitable for ongoing IT support, network management, or roles requiring deep knowledge of the company’s systems and processes. Employees in these roles can provide consistent support, handle emergencies, and ensure that the company’s technology infrastructure is maintained and updated regularly.
Marketing and creative services
Marketing and creative roles often lend themselves to independent contracting. For instance, a company might hire a freelance graphic designer to create a new logo, a copywriter to develop content for a marketing campaign or a social media strategist to plan a short-term promotion. These roles are typically project-based and can be completed independently.
On the other hand, hiring a salaried employee might be more effective for ongoing marketing efforts such as brand management, content creation, or customer engagement. A full-time marketing professional can develop a deep understanding of the company’s brand, maintain consistent messaging, and build long-term relationships with customers.
Finance and accounting
In finance and accounting, independent contractors are often brought in for tasks like auditing, tax preparation, or financial consulting. These roles require specialized knowledge and are often needed on a seasonal or as-needed basis.
However, for ongoing financial management, payroll processing, or roles that require regular interaction with other departments, a salaried employee may be more appropriate. Full-time finance professionals can provide consistent oversight of the company’s financial health, ensure compliance with regulations, and support strategic decision-making.
